Theme: An era to save natural resources of soil for future betterment
Geology Congress 2020
- Geological Researchers
- Geological Associations and Societies
- Scientists
- Young Researches
- Students
- Geoarchaeological officers
- Geology Engineers
- Professors
- Civil Engineers
- Research Scientists
- Engineering geologist
- Geochemist
- Geophysicist
- Geoscientist
- Geotechnical engineer
- Hydro geologist
- Mud logger
- Well site geologist
- Drilling engineer
- Environmental consultant
- Environmental engineer
- Minerals surveyors
Track: 1: Geology and Environmental Sustainability
Geology is about history that deals with solid earth and natural resources. Within the past we use to determine the volcanoes and earthquakes, and evolution, the fossil record we see within the rocks we'll analyze the geological time. Geologists are scientists who find most of the world’s natural resources and say the history of the earth. Environmental Sustainability is to preserve natural resources and develop alternate sources while reducing pollution towards the environment. Many of the projects that are entrenched in environmental Sustainability should include replantation of forests, stabilizing wetlands and shielding natural areas from resource harvesting, and thus the main criticism of environmental sustainability is to recruit the significances which can have probabilities with the need of a mounting commercial society. Environmental Sustainability is used to diminish the reduction of natural resources, and to plug the event without causing destruction to the environment. Geological conferences aim to inspire young researchers, geologists, and students.
Track 2: Geoscience Education
Geoscience is the scientific study of the earth and its geological systems. Geoscience deals with and investigation of Earth’s minerals, soil, water, and energy resources. Geoscience Education helps to review natural resources, teach us about the earth biographical nature and also does research on the resource we will get from the earth. Geoscience involves areas like volcanology, paleontology, or geochronology or they add a replacement emerging discipline like medical or forensic geology. Geoscience deals with the below modules.
Track 3: Geoarchaeology
Geoarchaeology is the sub-topic in geology. Archaeology is the study of the fabric remains of past human life and activities. The archaeological deals with artifacts, architecture, bio facts or Eco facts and cultural landscapes. Archaeological investigations are a primary source of data of prehistoric, ancient, and extinct cultures. Archaeology is often considered both science and a branch of the humanities. One among the main acquirements of 19th-century archaeology was the event of stratigraphy. One of the primary sites to undergo archaeological excavation was Stonehenge and other megalithic monuments in England.
Track 4: Engineering Geology
Engineering Geology knows about geological factors regarding the situation, design, construction, and operation. Engineering geologists provide conditional factors about geological and geotechnical recommendations, analysis, and style related to human development and various sorts of structures. Engineering geologist is actually within the area of investigation of how the world or earth processes impact human-made structures and human activities. Construction industries depend upon geological engineers to assure the steadiness of rock and soil foundations for tunnels, bridges, and high-rises. Foundations must withstand earthquakes, landslides, and everyone other phenomena that affect the bottom, including permafrost, swamps, and bogs.
Geological engineering finds better ways to create and manage landfills. They find safer ways to eliminate toxic chemicals and garbage and to manage sewage. They plan excavations and style tunnels.
Track 5: Environmental Geology
Environmental Geology is a sensible application regarding the principles of geology in the solving of environmental problems. It’s a multidisciplinary field that's closely associated with engineering geology and, to a lesser extent, to environmental geography.
Each of these fields involves the study of the interaction of humans with the geologic environment, including the biosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, and to some extent the atmosphere. Environmental geologists must have a solid understanding of not only currently occurring geologic events but historical geologic events, like past earthquakes and floods. this data of the past is vital because it helps them to urge a far better idea of what sorts of geologic events repeat themselves, with what frequency they could occur, and what sorts of damage occurred due to those events. Environmental geology may be a fundamentally important branch of science because it directly impacts every single person on the earth every single day. There are simply no thanks to avoiding the environment around you.
Track 6: Mining Engineering
Mining Engineering academically accomplished within the extraction of minerals from underneath the earth. Mining engineering is related to many other disciplines, like mineral extraction, exploration, excavation, geology, and metallurgy, geotechnical engineering and surveying. Mining Engineers will be working for resources to extract them from the earth like coal, minerals, petroleum, and other useful natural resources and lay out the plans, device shafts, inclines or quarries for the safe extraction of those resources from under the world. The natural resources are often coal, petroleum, metallic or nonmetallic minerals, etc.
Track 7: Geology in Civil Engineering
Civil engineering is the part of the engineering that deals with the construction & maintenance of roads, bridges, giant buildings, airports, ports, subways, dams, mines, and different giant-scale developments. For an engineering project to achieve success, the engineers should perceive the land upon that the project rests. Geologists study the land to work out whether or not it's stable enough to support the planned project. Some civil engineers use geologists to look at rocks for vital metals, oil, fossil fuel, and groundwater. The worth of earth science in mining has long been acknowledged however its use in engineering has been recognized solely in relatively recent years. Earth science provides scientific information on construction material, its prevalence, composition, durability, and different properties. For an example of such construction materials is building stones, road metal, clay, rock & dirt. The information on the geologic work of natural agencies like water, wind, ice and helps in coming up with and effecting major engineering works.
Track 8: Structural Geology
Structural geology is the study of the three-dimensional distribution of rock units with reference to their deformational histories. The aim of structural geology is to use measurements of present-day rock geometries to uncover information about the history of deformation (strain) within the rocks, and ultimately, to know the strain field that resulted in the observed strain and geometries. The study of geologic structures has been of prime importance in geology, both economic geology, and economic geology. Folded and faulted rock strata commonly form traps that accumulate and concentrate fluids like petroleum and gas.
Structural geology may be a critical part of engineering geology, which cares about the physical and mechanical properties of natural rocks. Structural geology works to find the damage present in the rocks like folds, foliations, and joints are internal weaknesses of rocks which can affect the steadiness of human-engineered structures like dams, road cuts, open-pit mines, and underground mines or road tunnels. Geotechnical risk, including earthquake risk, can only be investigated by inspecting a mixture of structural geology and geomorphology.
Track 9: Petroleum Geology
Petroleum geologists are scientists that employment to get new petroleum deposits. Petroleum geologists apply their knowledge on the world, and find its structures and analyze data to assist in locating and retrieving petroleum. Petroleum Geologists have the skill to read the story told by the very earth beneath our feet so as to seek out petroleum and other oils which are vital resources in our lives.
Petroleum geology is predominantly alarmed with the valuation of seven key features in sedimentary basins: They are the source, Reservoir, Seal, Trap, Timing, and Maturation Migration. Excesses oil migrating in the source will escape to the surface and seep. There are many ways the field of geology bestows are the need for the Petroleum Industry.
Track 10: Marine Geology
Marine geology is the study of the history and structure of the ocean bottom. The investigation of the ocean bottom and therefore the coastal zone. Marine geology has strong ties to geophysics or oceanology. Marine geology will be work on the ocean where they will study about water and its minerals present in marine water. The earth most of the population lives within 50 miles of the coast.
Track 11: Geographic Information System (GIS)
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) store, and analyze and visualize data for geographic positions on Earth’s surface. GIS is a computer-based tool that examines spatial relationships, patterns, and trends. By connecting geography with data, GIS better understands data employing a geographic context. GIS flourished within the 1980s. Common GIS operations include data acquisition, data management, data demand, vector data analysis, raster data analysis, and data display. A crucial tendency is that the integration of desktop GIS, web GIS, and mobile technology, which has already led to the event of location-based services, collaborative web-mapping, and volunteered geographic information.
Track 12: Soil and Ecosystem Services
Soil is the foundation of terrestrial ecosystems and therefore the majority of ecosystem services needed for human survival arise from soil. By deï¬nition, ecosystem services beneï¬t for human development and represent nature’s capital. for instance, the value of soil microbial metabolic pathways in removing greenhouse gases from the atmosphere, abating nutrients, eradicating pathogens and degrading organic pollutants has been estimated to be double that of the gross annual product.
The monetary valuation of those services, demanded by many governments and international agencies, is usually depicted as a necessary condition for the preservation of the natural capital that soils represent.
Track 13: Soil Preservation
Soil prevention is all about the prevention of soil loss from erosion due to chemicals present in soil and contamination. A sequel to deforestation is usually the large scale of erosion, loss of soil nutrients and sometimes total desertification.
Soil erosion removes the top soil that's necessary for organic matter, nutrients, micro-organisms that are required for plants to grow and shine. Soil Conservation is one such step that protects the soil from being washed away. The soil then finishes up in aquatic resources bringing in pesticides and fertilizers used on agricultural land. Healthy soil is vital for plants to grow and flourish. Taking the required steps to conserve the soil as a part of an environmentally friendly lifestyle. Soil conservation is a crucial part of sustainable agriculture and food production since it entails keeping soil from becoming a pollutant within the surface waters, and its ability to sieve and filter pollutants where we can improve the production.
Track 14: Gas Reservoirs
Gas reservoir, in geology and gas production, a present cargo area, characteristically a folded rock formation like an anticline, that traps and holds gas like petroleum. petroleum reservoirs are of two types they are conventional and unconventional reservoirs. Within the case of conventional reservoirs, the present hydrocarbons, like petroleum or gas, are trapped by overlying rock formations with lower permeability. While in unconventional reservoirs the rock has high porosity and low permeability which keeps the hydrocarbons trapped in situ, therefore not requiring a cap rock. Reservoirs are found using the hydrocarbon exploration method. Gas reservoir, in geology and gas production, a present stage area, characteristically a folded rock formation like an anticline that traps and holds the gas and it's to be capped by an impervious rock so as to make an efficient seal that forestalls the gas from escaping upward or laterally.
Track 15: Volcanology & Plate tectonics
A volcano is a gap within the crust that permits molten rock from the mantle to effuse onto the surface as lava. Volcanoes also emit vast amounts of gas, primarily CO2, water vapor, and sulfur dioxide. The solid particles present in the atmosphere will remain for years. The good majority of seismicity on the earth occurs at plate boundaries, although intra-plate seismicity can occur also when stresses build up within the plate. Volcanism is related to two of the plate boundary types: divergent and convergent margins. The previous manifest themselves as long volcanic rifts mostly within the ocean basins whereas the latter typically make individual volcanoes on the plate that "wins out" within the collision process (i.e., doesn't sub duct). Where two plates containing continental crust at their margins collide, there's little or no volcanism (such as at the Himalaya). Occasionally, plate boundaries where plates are mostly sliding by one another can experience small amounts of volcanism also if there's a component of extension across this boundary. Volcanism also can occur at intraplate volcanoes. These volcanoes are believed to possess sources deeper down within the Earth's mantle that remains during a relatively fixed location relative to the always migrating plate boundaries. Mauna Loa and Kilauea in Hawaii are the classic samples of intraplate volcanoes. Such volcanoes also can be seismically active, particularly when volcanic structures are built up rapidly. The crust must answer the additional load and relieves this stress through tectonic activity.
Track 16: Environmental Law
Environmental law is to protect the environmental pollution. Now environmental legal principles, specializing in the management of specific natural resources, like forests, minerals, or fisheries. Other areas, like environmental impact assessment. Now the Environmental law is taking care of each resource for the betterment of the environment.
1. Air Quality – Air quality laws protect the air from pollution and should include measures to guard the air from things like ozone depletion.
2. Water Quality – Environmental laws may protect water from pollution. They’ll also determine who can use water and the way to handle potential problems like treating wastewater and managing surface runoff.
Importance and Scope:
Geological survey plays an important role in conducting earth science, hydrologic, and natural hazards investigations and providing services that will be accustomed advise, inform, and educate stakeholders concerning the importance of earth sciences publicly policy selections. Geology survey plays a crucial role within the systematic assortment of geology information for ore dressing. Geology survey is important in obtaining magnetic and gravitational fields of the Earth's interior and topography. Increase in investments in mining and exploration activities may be a key issue boosting the demand for geology services across the world. Rise in demand for precious metals like gold, platinum, titanium, and silver is anticipated to drive the demand for geology services within the close to future. Minerals square measure being excavated at a quicker rate across the world so as to satisfy the wants of the rising population.
Members Associated with Geology Research:
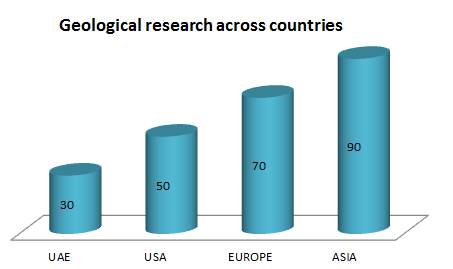
People are associated with geological research with many individual institutes, associations & societies, government bodies, in that most of them are professors, post-doc’s, PhD students along with individual scientists and also some of the museums are joining their hand in the field of geological research. Around 500 in Dubai, 2500 in UAE and more than 90,000 in the international level Physicians, Researchers and Academicians are working on the fields of Geology.
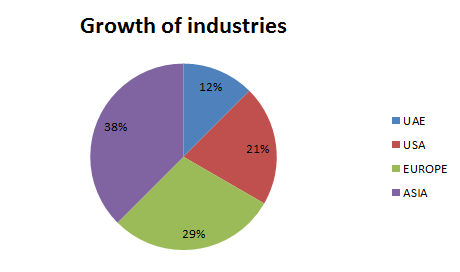
Growth of industries:
Companies and Industries associated to Geology are mining industries, oil and gas industries, coal industries and so on. Also many companies are there in UAE and in the globe which deals with Geological products. The graphical representation is the overall growth of industries in UAE, and Canada and in International level.
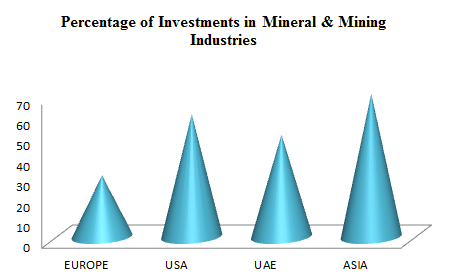
Investments in Mineral & Mining Industry:
The earth treatment advertises is surveyed to be regarded at USD 25.64 Billion out of 2016. It is foreseen to create at an above USD 43.65 billion of every 2025 and it is foreseen to create CAGR of 9.5% in the region of 2016 and 2025. With the extending care about sustenance security in North American, European, and Asian economies and contracting arable land, the enthusiasm for soil treatment things is depended upon to update the market improvement as soon as possible. The overall market is divided on the reason of its sorts into soil affirmation, regular changes, and pH operators.
The U.S. market for geosynthetics will reach nearly $2.4 billion in 2015 and nearly $2.8 billion by 2020, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.6% between 2015 and 2020.
The global oil storage market should reach $661.3 billion by 2023 from $617.2 billion in 2018 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1.4% for the period of 2018 to 2023.
The worldwide mining and oil and gas field producing business sector should reach $324.1 billion by 2020 from $265 billion of every 2016 at a compound yearly development rate (CAGR) of 5.2%, from 2016 to 2020
Geological Top Universities in Dubai
-
United Arab Emirates University
-
Khalifa University
-
University of Sharjah
-
Zayed University
-
Masdar Institute of Science and Technology
-
British University in Dubai
-
Heriot-Watt University
-
University of Birmingha
-
Sultan Qaboos University
-
King Abdulaziz University
-
King Saud University
-
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals
-
Petroleum Institute Abu Dhabi
-
King Abdullah University of Science & Technology
-
Sultan Qaboos University
Worldwide geological Universities
-
University Of British Columbia
-
University of Texas
-
University of Queensland
-
Duke Kunshan University (DKU)
-
University of St Thomas (Minnesota)
-
Kogakuin University
-
Shinshu University
-
University of Aberdeen
-
University of California Santa Cruz
-
University of St Andrews
-
Technical University Munich
-
Chalmers University of Technology
-
China University of Geosciences (Beijing)
-
University of Wisconsin – Madison
-
Kyungpook National University
-
National Autonomous University of Mexico
-
University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Vienna
-
Kyushu University
-
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
-
SUNY College of Environmental Science and Forestry
-
China University of Mining and Technology – Beijing
-
Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul
-
Guangdong University of Technology
-
Islamic Azad University
Related Societies:
USA:
American Association of Petroleum Geologists (AAPG), American Institute of Hydrology (AIH), Association of Environmental & Engineering Geologists (AEG), Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum (CIM), British Organic Geochemical Society, Society of Economic Geologists (SEG), Canadian Society of Exploration Geophysicists (CSEG), United States Geological Survey (USGS), Environmental and Engineering Geophysical Society, Geological Society of America (GSA), American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical and Petroleum Engineers (SME)
ASIA -PACIFIC:
Australian Geomechanics Society (AGS), Australian Society of Exploration Geophysicists (ASEG), Chinese Geophysical Society (CGS), Association of Exploration Geophysicists (AEG), Association of Petroleum Geologists (APG), Himpunan Ahli Geofisika Indonesia (HAGI), Society of Petroleum Geophysicists (SPG), Society of Exploration Geophysicists of Japan (SEGJ), Dhahran Geoscience Society (DGS), Emirates Society of Geosciences (ESG), Korean Society of Earth and Exploration Geophysicists (KSEG)
MIDDLE EAST:
Dhahran Geoscience Society (DGS), Emirates Society of Geosciences (ESG), Geological Survey of Iran (GSI), Jordan soil and land management web portal, saudi graphical society, Iranian Petroleum Geomechnicas Association (IPGA), Jordanian Geologists Association (JGA), Qatar Geological Section (QGS), Myanmar Geoscience Society (MGS), Turkish Association of Petroleum Geologists (TAPG)
EUROPE:
European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers, European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers, The Clay Minerals Society (CMS), German Geophysical Society (DGG), Geological Survey of Austria, Paleontological Research Institution (PRI), Society of Economic Geologists (SEG), Pittsburgh Association of Petroleum Geologists (PAPG), Australian Institute of Geoscientists (AIG), Australian Society of Exploration Geophysicists, Geoscience Information Society (GSIS), Geological Survey of Austria (GSA), Petroleum Exploration Society of Australia (PESA), Society for Sedimentary Geology (SEPM)
Related Conferences
-
International Conference on Geology & Geochemistry, November 23-24, 2020. Dubai, UAE
-
4th world summit on Renewable Energy and Resources, December 10-11, 2020, Dubai, UAE
-
10th International Conference on Environmental and Climate Change,September 21-22, 2020 Abu Dhabi, UAE
-
Global Conference on Sustainable Energy and Fuels ,December 10-11, 2020 Dubai, UAE
-
4th Annual Congress on Soil, Plant and Water Sciences, November 23-24, 2020 Barcelona, Spain
-
World Climate Change Conference, 09-10, 2020 Valencia, Spain
-
International Conference on Global Warming and Natural Disasters, June 01-02, 2020 Sydney, Australia
-
International Congress on Geotechnical Engineering and Geographic Information System, October 26- 27, 2020 Osaka, Japan
-
3rd International Conference on Renewable Energy and Resources, May 28-29, 2020, Vancouver, Canada
-
3rd Annual Expo on Soil, Water and Environmental sustainability, August 19-20,Frankfurt, German
Conference Highlights
- Geology and Environmental Sustainability
- Geoscience Education
- Geoarchaeology
- Engineering Geology
- Environmental Geology
- Mining Engineering
- Geology in Civil Engineering
- Structural Geology
- Petroleum Geology
- Marine Geology
- Geographic Information System (GIS)
- Soil and Ecosystem Services
- Soil Preservation
- Gas Reservoirs
- Volcanology & Plate tectonics
- Environmental Law
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | June 18-19, 2020 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Earth Science & Climatic Change
- Journal of Geography & Natural Disasters
- Journal of Geology & Geophysics
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by